created : 2021-11-07, updated : 2021-11-07
Introduction
이번 튜토리얼에서는 Dapr를 Kubernetes에 올려보겠다. dapr의 특징인 Service Invocation과 State Management 를 사용할 것이다.
Note. 본 소스는 Dapr 공식 Quick Start의 Hello-Kubernetes를 바탕으로 Dapr의 기능을 설명하기 위해 Application을 추가하여 작성하였다. 모두 Node.js 로 작성을 하였다.
Requirements
이전 Dapr 튜토리얼을 한번 보는 것은 좋겠다. 필수 사항은 아니고 본 튜토리얼을 따라가다 보면 자연스럽게 익힐 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
Dapr Installation: https://ahnchan.github.io/posts/CloudNative-Dapr-installation/
Dapr Quick Start - Hello World: https://ahnchan.github.io/posts/CloudNative-Dapr-QuickStart-HelloWorl/
Note. Kubernetes 의 설치는 Docker Desktop 에서 설정에서 Kubernetes를 Enable 시키면 된다.
Note. 외부 Kubernetes를 구성하고 싶으면 “Ansible을 이용하여 Ubuntu 20.04에 Kubernetes 구성하기”에서 간단하게 구성하는 설명을 해놓았다.
Pre-Installation
Dapr Installation: https://ahnchan.github.io/posts/CloudNative-Dapr-Installation/ Dapr Installation(Darp.io): https://docs.dapr.io/getting-started/ Docker: https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop Node.js: https://nodejs.org/en/download/ Heml : https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/ Redis : state store로 Redis를 사용한다. 그래서 Kubernetes 환경에서 Redis 설치가 필요하다. https://docs.dapr.io/getting-started/configure-state-pubsub/
Note. 이전 튜토리얼은 Self-Hosted이였다. Kubernetes 환경에서 깔끔하게 구동하려면 dapr uninstall –all 로 제거하고 진행하는 것도 좋을 것으로 생각된다.
구성
Gateway에서 node1, node2 로 Routing을 한다. 각각의 node는 /status 라는 상태를 체크하는 API를 제공하여 Node별로 잘 동작하는지 확인 할 수 있다.
/{NODE_NAME}/status: NODE_NAME은 gateway, nodoeapp1, nodeapp2이다. 각각에 status를 확인한다. 단순히 ok를 Return 하는 구조이다. /neworder: nodeapp2로 호출되며, 해당 정보를 nodeapp1로 전달하여 State Store에 order id를 저장한다. /order: nodeapp1을 호출하며, State Store에 저장된 Order Id를 조회 한다.
아래 Diagram은 /neworder를 호출할때의 흐름을 번호로 표시한 것이다. 소스를 확인해보면 gateway, nodeapp1, nodeapp2는 모두 자신(localhost)의 3500(Dapr Port)를 호출한다. 그러면 App Name을으로 해당 서비스(Application)를 호출을 한다.
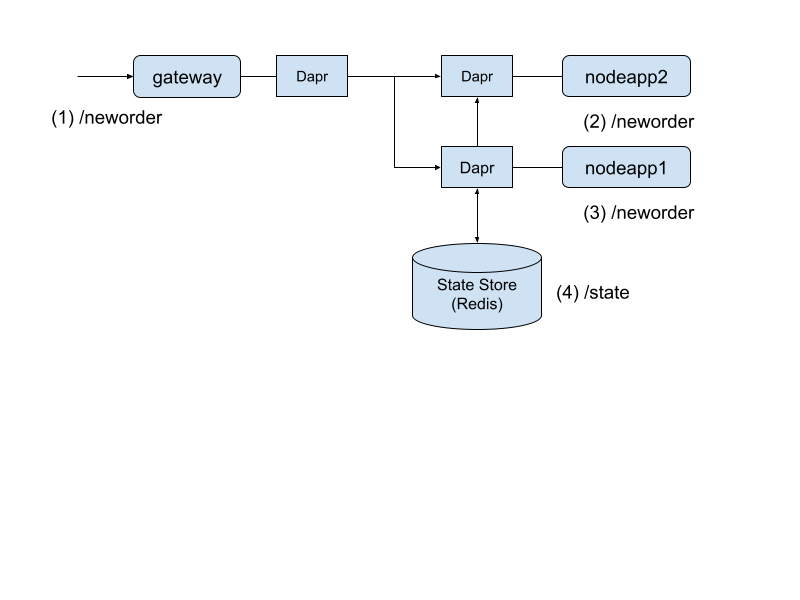
Note. 해당 소스는 https://github.com/ahnchan/tutorial-dapr-hello-kubernetes에 있으며, 소스에 대해 중요한 부분만 중간에 설명을 하겠다.
Redis 설치기
Redis는 State Store로 사용하며 Order의 Id를 저장한다. Helm을 이용하여 Kubernetes에 설치한다. 설치 문서 정보
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
$ helm repo update
$ helm install redis bitnami/redis
NAME: redis
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 8 13:12:24 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
...
Deployment
먼저 Local에 docker 이미지 생성한다. 각각의 디렉토리 (/nodegateway, /node1, /node2)에서 실행을 한다.
1
2
$ cd nodegateway
$ npm run docker-build
Note. Docker 이미지는 docker images 로 확인할 수 있다.
Docker 이미지가 잘 만들어졌으면, 이제 Kubernetes에 Deploy를 해보자.
1
2
$ cd ../deploy
$ kubectl apply -f .
모두 정상적으로 되었으면 아래와 같이 확인 할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
$ kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 10d
nodeapp1-dapr ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,9090/TCP 39m
nodeapp2-dapr ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,9090/TCP 6m23s
nodegateway LoadBalancer 10.105.151.114 localhost 80:31292/TCP 40m
nodegateway-dapr ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,9090/TCP 40m
redis-headless ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP 89m
redis-master ClusterIP 10.96.111.168 <none> 6379/TCP 89m
redis-replicas ClusterIP 10.103.174.207 <none> 6379/TCP 89m
zipkin ClusterIP 10.110.155.108 <none> 9411/TCP 80m
테스트하기
각 Application의 status 를 확인해보자. 해당 Application 이 Deploy가 잘 되었는지 알수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
$ curl http://localhost/order/status
{
“status”: “ok”
}
$ curl http://localhost/neworder/status
{
“status”: “ok”
}
$ curl http://localhost/gateway/status
{
“status”: “ok”
}
이번에는 State Store에 order 정보를 저장해보자. neworder로 Order를 저장을 요청 한다. sample.json을
파일: sample.json
1
2
{"data":{"orderId":"42"}}
1
$ curl --request POST --data @sample.json --header Content-Type:application/json http://localhost/neworder
이제 저장된 Order를 확인해 보자.
1
2
3
4
$ curl http://localhost/order
{
"orderId": "42"
}
소스 확인해보기
동작되는 것을 확인해보았으니 Source를 한번 보자.
Gateway에서 nodeapp2로 Routing하기
gateway는 외부에서 들어오는 API 요청을 해당 Application 으로 Routing해주는 일을 한다.
위치: /nodegateway 파일: app.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
const daprUrl = `http://localhost:${daprPort}/v1.0/invoke`;
const orderUrl = daprUrl + "/nodeapp1/method";
const neworderUrl = daprUrl + "/nodeapp2/method";
// Node1 /order
app.get('/order', async (req, res) => {
const url = `${orderUrl}/order`;
req.pipe(request(url)).pipe(res);
});
// Node2 /neworder
app.post('/neworder', async (req, res) => {
const url = `${neworderUrl}/neworder`;
req.pipe(request(url)).pipe(res);
});
/order (nodeapp1), /neworder(nodeapp2) 모두 localhost:${daprPort} 를 호출한다. nodeapp1, nodeapp2의 실제 서버가 어디에 있던지 Path를 v1.0/invoke/nodeapp1 으로 해당 Application을 명시할 수 있다.
Nodeapp2에서 nodeapp1 호출하기
/neworder이 gateway를 통해서 nodeapp2 로 전달이 된다. 그러면 nodeapp1으로 다시 호출을 한다.
Note. Dapr를 설명하기 위해 임의로 구현한 작성한 코드이다. 실제 환경이면 직접 nodeapp1을 호출하는게 맞을 것이다.
위치: /node2 파일: app.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
const stateUrl = `http://localhost:${daprPort}/v1.0/invoke/nodeapp1/method/neworder`;
...
app.post('/neworder', (req, res) => {
const data = req.body;
const orderId = data.orderId;
console.log("Got a new order! Order ID: " + orderId);
console.log("url: "+ stateUrl);
console.log("state: "+ JSON.stringify(data));
fetch(stateUrl, {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(data),
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
/neworder 로 호출된 정보는 stateUrl이라는 nodeapp1에 정의된 /neworder를 호출하게 되어 있다. stateUrl에서 보듯이 nodeapp2에서도 localhost의 Dapr Port를 호출하게 되어 있다.
Nodeapp1에서 State 저장
nodeapp1에서는 State Store에 정보를 저장한다.
위치: /node1 파일: app.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
const stateUrl = `http://localhost:${daprPort}/v1.0/state/${stateStoreName}`;
…
app.post('/neworder', (req, res) => {
const data = req.body.data;
const orderId = data.orderId;
console.log("Got a new order! Order ID: " + orderId);
const state = [{
key: "order",
value: data
}];
fetch(stateUrl, {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(state),
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
/neworder는 State Store에 Order ID를 저장한다. State Store도 Dapr의 API를 호출하여 Key, Value 형태로 저장을 한다. stateUrl이 localhost의 Dapr 포트를 호출하고 /v1.0/state 로 State Store를 명시하고 있다.
저장된 order 정보는 /order로 확인을 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
const stateUrl = `http://localhost:${daprPort}/v1.0/state/${stateStoreName}`;
...
app.get('/order', (_req, res) => {
console.log('/order');
fetch(`${stateUrl}/order`)
.then((response) => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw "Could not get state.";
}
return response.text();
}).then((orders) => {
res.send(orders);
}).catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
res.status(500).send({message: error});
});
});
등록된 Application, Service 정리하기
튜토리얼을 종료하고 정리를 해보자. 새로 생성한 pods, service를 삭제를 한다.
1
2
$ cd deploy
$ kubectl delete -f .
Redis 서비스도 삭제 한다.
1
$ helm uninstall redis
Conclusions
Dapr의 가장 기본적인 기능을 확인해봤다. 서비스의 위치를 알지 못해도, Application 이름으로만 API를 호출할 수가 있다. 또한 State Store를 기본 제공하고 있어서 어느 앱에서나 State Store를 Dapr의 API만을 이용하여 접근이 가능해 진다. Dapr는 API를 호출하는 방식이기 때문에 어떤 언어든 상관없이 사용이 가능하다. 특별한 SDK, Library없이 Dapr를 이용하면 여러가지 언어로 Micro Service를 구현할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
References
Dapr Quick Start - Hello Kubernetes